- Lentinan
-
Lentinan
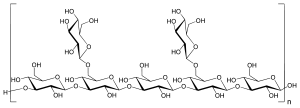
Nombre (IUPAC) sistemático β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-[β-D-glucopiranosil-(1→3)-[β-D-glucopiranosil-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopiranosil-(1→3)-β-D-glucopiranosil-(1→3)β-D-glucopiranosil-(1→3)]-β-D-glucopiranosa General Otros nombres (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6S)-3,5-dihidroxi-2-(hydroximetil)-6-[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2,3,5-trihidroxi-6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihidroxi-6-(hidroximetil)oxan-2-yl]oximetil]oxan-4-il]oxioxan-4-il]oxi-3,5-dihidroxi-6-(hidroximetil)oxan-4-il]oxi-3,5-dihidroxi-6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-4-yl]oxy-6-(hidroxietil)oxane-3,4,5-triol Fórmula molecular n/d Identificadores Número CAS 37339-90-5 Código ATC L03AX01 PubChem Propiedades físicas Masa molar 1152.99948 g/mol Propiedades químicas Valores en el SI y en condiciones normales
(0 °C y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario.
Exenciones y referenciasLentinan es un beta-glucano con un vinculación glucosídica β-1, 3: β-1, 6[1] Se trata de un polisacárido antitumoral de la seta shiitake (Lentinula edodes) .[1] Lentinan es un polisacárido que tiene un peso molecular de aproximadamente 500.000 Da. La compañía farmacéutica japonesa Ajinomoto desarrolló Lentinan, un agente administrado por vía intravenosa contra el cáncer.[2]
Contenido
Descripción
Lentinan es uno de los fármacos contra el cáncer[3] que se ha demostrado que afectan a los sistemas de respuesta inmune del huésped.[4]
La investigación sobre los efectos de Lentinan
Un experimento in vitromostró que lentinan estimula la producción de glóbulos blancos en la línea celular humana U937.[5] Una combinación farmacológica (MC-S) de lentinan, PSK, Ganoderma lucidum y Astragalus propinquus , también ha demostrado estimular la producción de glóbulos blancosin vitro.[6]
Un experimento in vivo en ratones, reveló que Lentinan es activo por vía oral (ya que el uso clínico del fármaco es por administración vía intravenosa).[7] Los limitados estudios clínicos de pacientes con cáncer han asociado a lentinan con una tasa de supervivencia más alta, mayor calidad de vida, y a menor reincidencia de cáncer.[8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15]
Véase también
- Hongos medicinales
- Shiitake
Referencias
- ↑ a b cáncer Guía Incluye muchos resúmenes
- ↑ Letnan en Cancer Research
- ↑ Nakano H, Namatame K, Nemoto H, Motohashi H, Nishiyama K, Kumada K (1999). «A multi-institutional prospective study of lentinan in advanced gastric cancer patients with unresectable and recurrent diseases: effect on prolongation of survival and improvement of quality of life. Kanagawa Lentinan Research Group.». Hepatogastroenterology 46 (28): pp. 2662–8. PMID 10522061.
- ↑ Nakano H, Namatame K, Nemoto H, Motohashi H, Nishiyama K, Kumada K (1999). «A multi-institutional prospective study of lentinan in advanced gastric cancer patients with unresectable and recurrent diseases: effect on prolongation of survival and improvement of quality of life. Kanagawa Lentinan Research Group». Hepatogastroenterology 46 (28): pp. 2662–8. PMID 10522061.
- ↑ Sia GM, Candlish JK. (Mar 1999). «Effects of shiitake (Lentinus edodes) extract on human neutrophils and the U937 monocytic cell line.». Phytother Res. 13 (2): pp. 133–7. doi:. PMID 10190187
- ↑ Clark D, Adams M. (2007). «Using commercial nutraceutical mixes as immune stimulants: an in vitro proliferation study using Metabolic Cell-Support on non-stimulated human lymphocytes.». Austr. J. Med. Herbal. 19: pp. 108–111
- ↑ Ng ML, Yap AT. (Oct 2002). «Inhibition of human colon carcinoma development by lentinan from shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes).». J Altern Complement Med. (National University of Singapore) 8 (5): pp. 581–9. doi:. PMID 12470439
- ↑ Yang P, Liang M, Zhang Y, Shen B. (Aug 2008). «Clinical application of a combination therapy of lentinan, multi-electrode RFA and TACE in HCC.». Adv Ther. 25 (8): pp. 787–94. doi:. PMID 18670743
- ↑ Nimura H, Mitsumori N, Takahashi N, (Jun 2006). «[S-1 combined with lentinan in patients with unresectable or recurrent gastric cancer]». Gan to Kagaku Ryoho. 33 (1): pp. 106–9. PMID 16897983
- ↑ Nakano H, Namatame K, Nemoto H, Motohashi H, Nishiyama K, Kumada K. (1999). «A multi-institutional prospective study of lentinan in advanced gastric cancer patients with unresectable and recurrent diseases: effect on prolongation of survival and improvement of quality of life. Kanagawa Lentinan Research Group.». Hepatogastroenterology. 46 (28): pp. 2662–8. PMID 10522061
- ↑ Oba K, Kobayashi M, Matsui T, Kodera Y, Sakamoto J (July 2009). «Individual Patient Based Meta-analysis of Lentinan for Unresectable/Recurrent Gastric Cancer». Anticancer Res. 29 (7): pp. 2739–45. PMID 19596954.
- ↑ Hazama S, Watanabe S, Ohashi M, et al. (July 2009). «Efficacy of Orally Administered Superfine Dispersed Lentinan ({beta}-1,3-Glucan) for the Treatment of Advanced Colorectal Cancer». Anticancer Res. 29 (7): pp. 2611–7. PMID 19596936.
- ↑ Kataoka H, Shimura T, Mizoshita T, et al. (2009). «Lentinan with S-1 and paclitaxel for gastric cancer chemotherapy improve patient quality of life». Hepatogastroenterology 56 (90): pp. 547–50. PMID 19579640.
- ↑ Isoda N, Eguchi Y, Nukaya H, et al. (2009). «Clinical efficacy of superfine dispersed lentinan (beta-1,3-glucan) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma». Hepatogastroenterology 56 (90): pp. 437–41. PMID 19579616.
- ↑ Shimizu K, Watanabe S, Watanabe S, et al. (2009). «Efficacy of oral administered superfine dispersed lentinan for advanced pancreatic cancer». Hepatogastroenterology 56 (89): pp. 240–4. PMID 19453066.
Enlaces externos
- Efectos antitumorales de Lentinan (y otros)
- Smith JE, Rowan NJ, Sullivan R Hongos medicinales: sus propiedades terapéuticas y de uso médico actual con especial énfasis en tratamientos para el cáncer Cancer Research UK, 2001
- Página de Lentinan del Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.
Categorías:- Polisacáridos
- Inmunoestimulantes
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.
