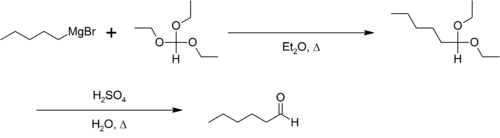- Síntesis de aldehídos de Bodroux-Chichibabin
-
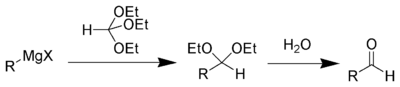
La Síntesis de aldehídos de Bodroux-Chichibabin El es una reacción química en la cual un reactivo de Grignard se transforma en un aldehído homólogo al halogenuro original.
La reacción del reactivo de Grignard con ortoformiato de trietilo da como producto un acetal, que puede ser hidrolizado a un aldehído. Por ejemplo, la síntesis de n-hexaldehído.[1]
Véase también
Referencias
- ↑ G. Bryant Bachman (1943). "n-Hexaldehyde". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 2: 323.
- Bodroux, F. (1904). Compt. Rend. 138: pp. 92.
- Tschitschibabin, A. E. (1904). «Eine neue allgemeine Darstellungsmethode der Aldehyde». Ber. 37: pp. 186. doi:.
- Tschitschibabin, A. E. (1904). «Ueber den Hexahydro-m-toluylaldehyd». Ber. 37: pp. 850. doi:.
- Smith, L. I.; Bayliss, M. (1941). «The Bodroux-Tschitschibabin, and the Bouveault Aldehyde Syntheses». J. Org. Chem. 6: pp. 437. doi:.
- Smith, L. I.; Nichols, J. (1941). «The Synthesis of Aldehydes from Grignard Reagents. II. Polymethylbenzaldehydes». J. Org. Chem. 6: pp. 489. doi:.
Categoría:- Reacciones químicas orgánicas
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.