- Fisiología respiratoria
-
Fisiología respiratoria
La Fisiología respiratoria es la rama de la fisiología humana que se enfoca en el proceso de respiración
Los temas de estudio incluyen:
Contenido
Volúmenes
- Volúmenes pulmonares
- Capacidad vital
- Capacidad residual funcional
- Espacio muerto
- Espirometría
- Pletismografía corporal
- Fluxo máximo
Mecanismo de la respiración
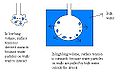
La Inspiración consiste generalmente en un movimiento activo. La contracción del diafragma produce un aumento del volumen de manera anteroposterior y vertical, lo que produce un cambio de presión, el que equivale a las presiones producidas por los componentes elásticos, resistivos e inerciales del sistema respiratorio, principalmente del parénquima pulmonar y la pared toráxica
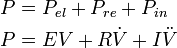
Where Pel equals the product of elastance E (inverse of compliance) and volume of the system V, Pre equals the product of flow resistance R and time derivate of volume V (which is equivalent to the flow), Pin equals the product of inertance I and second time derivate of V. R and I are sometimes referred to as Rohrer's constants.
- Anatomia: cavidad pleural, thoracic diaphragm, Intercostales externi muscles, Intercostales interni muscles
- inspiración y espiración
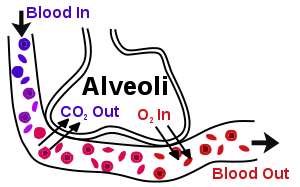
- lung, alveolos pulmonares
- With insufficient pulmonary surfactant, the pulmonary alveoli collapse, causing atelectasis (in infants, infant respiratory distress syndrome)
- the law of Laplace,
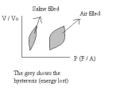
- compliance (physiology) - decreased with fibrosis, increased with emphysema[1]
- Poiseuille's law
- asthma and COPD
- hysteresivity
Circulación, ventilación y perfusión
- pulmonary circulation
- positive pressure ventilation
- hypoxic vasoconstriction
- ventilation (physiology), perfusion, ventilation/perfusion ratio (V/Q), and ventilation/perfusion scan
- shunts: right-to-left (tetralogy of fallot), left-to-right (patent ductus arteriosus)
- respiratory rate and respirometer
Intercambio gaseoso (principalmente oxígeno y dióxido de carbono)
- gas exchange
- Dalton's law
- hemoglobin
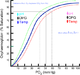
- oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, Bohr effect, Haldane effect
- carbonic anhydrase
- oxyhemoglobin
- respiratory quotient
- arterial blood gas
Control y regulación
- control of respiration
- reticular formation
- pons (apneuistic and pneumotaxic)
- chemoreceptors (medulla, carotid body, aortic body)
- Hering-Breuer reflex
- involuntary control of respiration
- exercise
- hyperoxia
- hypoxemia (hypoxic hypoxia)
Fisiopatología
- altitude sickness
- asthma
- carbon monoxide poisoning
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- emphysema
- infant respiratory distress syndrome
- pulmonary edema
Véase también
- breath sounds
- pulmonology
- respiratory system
- Wikipedia:MeSH G09#MeSH G09.772 --- respiratory physiology
Imágenes adicionales
Referencias
Enlaces externos
Categoría: Respiración
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.