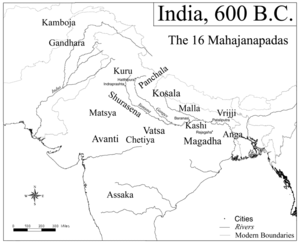
- Mahajanapadas
-
Los maja yana padás fueron varios reinos que coexistieron en el norte y noroeste de la India, a mediados del I milenio a. C.
- mahājanapada en escritura devánagari.
- महाजनपद en el sistema AITS (alfabeto internacional de transliteración sánscrita).
- Pronunciación: majá yána padá[1]
Contenido
Etimología
Literalmente significa ‘grandes reinos‘ (del sánscrito mahā: ‘gran’, yana-padá: comunidad, nación, pueblo, súbditos (lo opuesto al soberano), imperio, país habitado, siendo yana: ‘gente, tribu’, y pada: ‘lugar’.[1]
Historia
El antiguo texto budista Anguttara nikaya (I. pág. 213; IV. los pp 252, 256, 261) hacen referencia frecuente a dieciséis grandes reinos (ṣoḍaśa [dieciséis] maha-jana-pada) que se habían desarrollado y habían prosperado en la zona norte y noroeste del subcontinente indio antes de la expansión del budismo en la India (o sea, antes del siglo VI a. C.). No menciona ninguna historia, excepto en el caso de Magadha. El libro budista Anguttara nikaya, en varios lugares, da una lista de estas dieciséis naciones:
- Anga
- Asaka
- Avanti
- Chedi
- Gandhara
- Kamboya
- Kasi
- Kosala
- Kuru
- Matsia (o Machcha)
- Magadha
- Mal•la
- Panchala
- Shúrasena
- Vayyi (o Vriyi)
- Vatsa (o Vamsa)
Otro texto budista, el Digha nikaia (vol. II, pág. 200) menciona solamente los primeros doce mahajanapadas y omite los cuatro restantes en la lista antedicha.
El Chulla niddesa, otro texto antiguo del canon budista, agrega Kalinga a la lista y menciona a Iona en lugar de Gandhara; así enumera a Kamboja y Yona como el único majayanapada de Uttarapatha.
El texto yaina Bhagavati-sutra lista brevemente 16 majá yanapadás: Achja, Anga, Avaja, Bayyi (Vayyi), Banga (Vanga, actual Bengala), Kasi, Koch•cha (Kach•cha), Koshala, Ladha (Lata), Magadha, Malavaka, Malaia, Moli (Mal•la), Padha, Sambhuttara y Vachja.
Obviamente, el autor del Bhagavati-sutra tiene su foco en los países de Madhiesa y del sur y extremo Oriente solamente. El autor omite las naciones de Uttarapatha (como Kamboja y Gandhara). El horizonte más extendido de Bhagavati y la omisión de todos los países de Uttarapatha demuestra claramente que la lista de Bhagavati tiene un origen tardío y por lo tanto menos confiable.[2]
Error en internet
Se desconoce la razón por la que en internet se dice que eran repúblicas, sin rey. Las únicas referencias conocidas dicen que eran monarquías hereditarias.
Notas
- ↑ a b Según el Sanskrit-English Dictionary del británico Monier Monier-Williams (1819-1899).
- ↑ Historia política de la India antigua (pág. 86), 1996; Historia y cultura de la gente india, de la edad de la unidad imperial (pág. 15 y 16).
Categorías:- Historia de los pueblos del sur de Asia
- Historia de la India
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.