- Pfiesteria
-
Pfiesteria
?Pfiesteria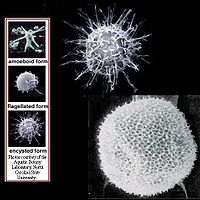
Clasificación científica Reino: Protista Filo: Dinoflagellata Clase: Blastodiniophyceae Orden: Blastodiniales Familia: Oodiniaceae Género: Pfiesteria Especies Pfiesteria piscicida
Pfiesteria shumwayaePfiesteria es un género de dinoflagelados heterótrofos que se asocia con la proliferación algal y la mortalidad de peces. Se ha propuesto que Pfiesteria fue el responsable de la gran mortalidad de peces de las costas de Carolina del Norte y del estuario de la Bahía Chesapeake en 1980s y 1990s. En respuesta a estos brotes tóxicos, seis estados de la costa este de EE.UU. iniciaron un programa de monitorización para disponer una respuesta rápida en el caso de nuevos brotes tóxicos y para comprender mejor los factores que influyen en la toxicidad de Pfiesteria.[1] Con los nuevos métodos de detección molecular, se ha determinado que Pfiesteria tiene una distribución mundial.[2]
Contenido
Descubrimiento
Pfiesteria fue descubierto en 1988 por investigadores de la Universidad Estatal de Carolina del Norte y lleva su nombre en honor a Lois Ann Pfiester (1936–1992), una bióloga que hizo gran parte de las primeras investigaciones sobre dinoflagelados. Una historia en profundidad del descubrimiento puede encontrase en And the Waters Turned to Blood by Rodney Barker.[3]
Estrategia de alimentación
Las primeras investigaciones llegaron a la hipótesis de que Pfiesteria actúa como un depredador utilizando una toxina que paraliza el sistema respiratorio de los peces susceptibles tales como menhaden, a los que causa la muerte por anoxia. A continuación consume los tejidos de su presa muerta.[4]
Controversia
La biología de Pfiesteria y su rol en la mortalidad de peces y en la salud humana han estado sujetos a controversia debido a investigaciones de resultados contradictorios en los últimos años.[5] [6]
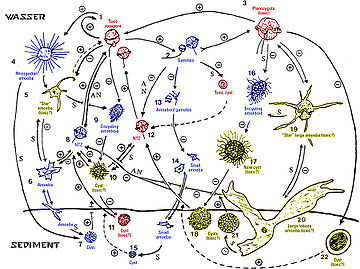
- Ciclo vital: Las primeras investigaciones que establecían un ciclo vital complejo de Pfiesteria piscicida están discutidas debido a resultados contradictorios obtenidos en investigaciones de los últimos años, especialmente sobre la cuestión de la existencia o no de una forma ameboide tóxica.[7]
- Toxicidad: La hipótesis de que Pfiesteria mata a los peces segregando toxinas en el agua ha sido cuestionada puesto que esta no ha podido ser aislada en varios experimentos. La toxicidad parece depender de las cepas y de los ensayos realizados.[8] A principios de 2007 fue identificada una toxina altamente inestable producida por la forma tóxica de Pfiesteria piscicida.[9]
- Lesiones en la piel: Las lesiones observadas sobre los peces presumiblemente matados por Pfiesteria ha sido atribuidos a oomicetes por algunos investigadores. Sin embargo, también se ha establecido que Pfiesteria shumwayae mata a los peces al alimentarse de su piel mediante microdepredación.[10]
- Impacto sobre la salud humana: Los efectos en humanos han sido cuestionados a finales de 1990 atribuyéndolos a la histeria.[11] Sin embargo fueron corroborados por una evaluación posterior.[12] La controversia sobre los efectos en la salud humana de la exposición a Pfiesteria todavía continúa.[13] [14]
Referencias
- ↑ Magnien RE (2001). «State monitoring activities related to Pfiesteria-like organisms» Environ. Health Perspect.. Vol. 109 Suppl 5. pp. 711–4. PMID 11677180.
- ↑ Rublee PA, Remington DL, Schaefer EF, Marshall MM (2005). «Detection of the Dinozoans Pfiesteria piscicida and P. shumwayae: a review of detection methods and geographic distribution» J. Eukaryot. Microbiol.. Vol. 52. n.º 2. pp. 83–9. DOI 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2005.05202007.x. PMID 15817112.
- ↑ Barker, Rodney. And the Waters Turned to Blood. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-83845-1.
- ↑ Eichhorn, Susan E.; Raven, Peter H.; Evert, Ray Franklin (2005). Biology of plants. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, pp. 205. ISBN 0-7167-1007-2.
- ↑ «Pfiesteria: Frequently Asked Questions». Consultado el 2008-01-06.
- ↑ Miller TR, Belas R (2003). «Pfiesteria piscicida, P. shumwayae, and other Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellates» Res. Microbiol.. Vol. 154. n.º 2. pp. 85–90. DOI 10.1016/S0923-2508(03)00027-5. PMID 12648722.
- ↑ Peglar MT, Nerad TA, Anderson OR, Gillevet PM (2004). «Identification of amoebae implicated in the life cycle of Pfiesteria and Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellates» J. Eukaryot. Microbiol.. Vol. 51. n.º 5. pp. 542–52. PMID 15537089.
- ↑ Burkholder JM, Gordon AS, Moeller PD, et al (2005). «Demonstration of toxicity to fish and to mammalian cells by Pfiesteria species: comparison of assay methods and strains» Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.. Vol. 102. n.º 9. pp. 3471–6. DOI 10.1073/pnas.0500168102. PMID 15728353.
- ↑ Moeller PD, Beauchesne KR, Huncik KM, Davis WC, Christopher SJ, Riggs-Gelasco P, Gelasco AK (2007). «Metal complexes and free radical toxins produced by Pfiesteria piscicida» Environ. Sci. Technol.. Vol. 41. n.º 4. pp. 1166-72. PMID 17598275.
- ↑ Vogelbein WK, Lovko VJ, Shields JD, et al (2002). «Pfiesteria shumwayae kills fish by micropredation not exotoxin secretion» Nature. Vol. 418. n.º 6901. pp. 967–70. DOI 10.1038/nature01008. PMID 12198545.
- ↑ Greenberg DR, Tracy JK, Grattan LM (1998). «A critical review of the Pfiesteria hysteria hypothesis» Md Med J. Vol. 47. n.º 3. pp. 133–6. PMID 9601200.
- ↑ Collier DN, Burke WA (2002). «Pfiesteria complex organisms and human illness» South. Med. J.. Vol. 95. n.º 7. pp. 720–6. PMID 12144078.
- ↑ Morris JG, Grattan LM, Wilson LA, et al (2006). «Occupational exposure to pfiesteria species in estuarine waters is not a risk factor for illness» Environ. Health Perspect.. Vol. 114. n.º 7. pp. 1038–43. PMID 16835056.
- ↑ Shoemaker RC, Lawson W (2007). «Pfiesteria in estuarine waters: the question of health risks» Environ. Health Perspect.. Vol. 115. n.º 3. pp. A126–7. PMID 17431460.
Enlaces externos
 Wikimedia Commons alberga contenido multimedia sobre Pfiesteria.
Wikimedia Commons alberga contenido multimedia sobre Pfiesteria.
Categoría: Blastodiniales
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.