- Glyptothorax
-
Glyptothorax
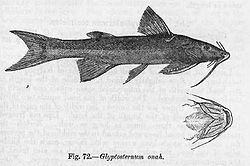
Glyptothorax lonah.Clasificación científica Reino: Animalia Filo: Chordata Clase: Actinopterygii Orden: Siluriformes Superfamilia: Sisoroidea Familia: Sisoridae Subfamilia: Glyptosterninae Tribu: Glyptothoracini
de Pinna, 1996Género: Glyptothorax
Blyth, 1860Especies Alrededor de 70. Consultar la sección «Especies».
Sinonimia Glyptothorax es un género de peces gato (orden Siluriformes) de la familia Sisoridae. Es el género más abundante en especies y de distribución más amplia de la familia, con más de 70 especies descritas y aún más por descubrir.
Contenido
Distribución
Las especies de Glyptothorax se encuentran en la cuenca hidrográfica del mar Negro, norte de Turquía, sur y este de la cuenca del río Yangtze en China y sur de Indochina hasta Java (Indonesia).[1] Se les encuentra también en Asia Menor (cuencas de los ríos Tigris y Éufrates) hasta el Sudeste Asiático. El género es muy diverso en el Subcontinente Indio.[2] Las especies del sudeste de Asia tienden a tener unas distribuciones mas restringidas.[3]
Descripción
Glyptothorax se distingue fácilmente de otros sisóridos por el aparato adhesivo torácico que poseen, cuyos surcos recorren al animal paralela u oblicuamente a su eje longitudinal, al contrario que en otros géneros en los que los surcos son transversales, o bien en los que este aparato se encuentra totalmente ausente.[1] Las aletas dorsales y pectorales tienen fuertes espinas. La espina de la aleta dorsal es lisa o bien aserrada en la parte anterior y lisa o más finamente aserrada en la parte posterior, mientras que la de la aleta pectoral es aserrada siempre. La cabeza es pequeña y aplastada y el hocico cónico. El cuerpo es alargado y plano, pudiendo ser muy aplastado en ocasiones. La piel es lisa o granulada. Los ojos son pequeños y están situados a los lados de la cabeza. Los labios son gruesos, carnosos y a menudo poseen papillas. Las barbas maxilares tienen una membrana bien desarrollada y una base suave. Las aberturas de las branquias son amplias. Las aletas pares son trenzadas y se encuentran modificadas para formar el aparato adhesivo que poseen algunas especies del género.[1]
Ecología
Como otras especies de sisóridos, estos peces son reófilos, es decir, prefieren las corrientes rápidas como hábitat, para las que su aparato adhesivo supone una adaptación, permitiéndoles fijarse a las rocas y evitando que sean arrastrados por la corriente.[3]
Especies
Actualmente se reconocen 75 especies:[4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]
- Glyptothorax annandalei (Hora, 1923)
- Glyptothorax armeniacus (Berg, 1918)
- Glyptothorax botius (Hamilton, 1822)[11]
- Glyptothorax brevipinnis (Hora, 1923)
- Glyptothorax buchanani (Smith, 1945)
- Glyptothorax callopterus (Smith, 1945)
- Glyptothorax cavia (Hamilton, 1822)
- Glyptothorax chindwinica (Vishwanath & Linthoingambi, 2007)[12]
- Glyptothorax conirostre (Steindachner, 1867)
- Glyptothorax coracinus (Ng & Rainboth, 2008)[13]
- Glyptothorax cous (Linnaeus, [[1766)
- Glyptothorax davissinghi (Manimekalan & Das, 1998)[14]
- Glyptothorax deqinensis (Mo & Chu, 1986)
- Glyptothorax dorsalis (Vinciguerra, 1890)
- Glyptothorax exodon (Ng & Rachmatika, 2005)[15]
- Glyptothorax filicatus (Ng & Freyhof, 2008)[16]
- Glyptothorax fokiensis (Rendahl, 1925)[17]
- Glyptothorax fuscus (Fowler, 1934)
- Glyptothorax garhwali (Tilak, 1969)
- Glyptothorax gracilis (Günther, 1864)
- Glyptothorax granulus (Vishwanath & Linthoingambi, 2007)[12]
- Glyptothorax honghensis (Li, 1984)
- Glyptothorax housei (Herre, 1942)[18]
- Glyptothorax indicus (Talwar, 1991)
- Glyptothorax interspinalum (Mai, 1978)
- Glyptothorax jalalensis (Balon & Hensel, 1970)[19]
- Glyptothorax kashmirensis (Hora, 1923)
- Glyptothorax kurdistanicus (Berg, 1931)
- Glyptothorax laak (Popta, 1904)
- Glyptothorax lampris (Fowler, 1934)
- Glyptothorax laosensis (Fowler, 1934)
- Glyptothorax lonah (Sykes, 1839)[20]
- Glyptothorax longicauda (Li, 1984)
- Glyptothorax longjiangensis (Mo & Chu, 1986)
- Glyptothorax macromaculatus (Li, 1984)
- Glyptothorax madraspatanum (Day, 1873)
- Glyptothorax major (Boulenger, 1894)
- Glyptothorax manipurensis (Menon, 1955)
- Glyptothorax minimaculatus (Li, 1984)
- Glyptothorax minutus (Hora, 1921)
- Glyptothorax naziri (Mirza & Naik, 1969)
- Glyptothorax nelsoni (Ganguly, Datta & Sen, 1972)
- Glyptothorax ngapang (Vishwanath & Linthoingambi, 2007)[12]
- Glyptothorax nieuwenhuisi (Vaillant, 1902)
- Glyptothorax obscura (Li, 1984)
- Glyptothorax pallozonum (Lin, 1934)
- Glyptothorax panda (Ferraris & Britz, 2005)[21]
- Glyptothorax pectinopterus (McClelland, 1842)
- Glyptothorax platypogon (Valenciennes, 1840)
- Glyptothorax platypogonides (Bleeker, 1855)
- Glyptothorax plectilis (Ng & Hadiaty, 2008)[22]
- Glyptothorax poonaensis (Hora, 1938)
- Glyptothorax prashadi (Mukerji, 1932)
- Glyptothorax punjabensis (Mirza & Kashmiri, 1971)
- Glyptothorax quadriocellatus (Mai, 1978)
- Glyptothorax rugimentum (Ng, 2008)[23]
- Glyptothorax saisii (Jenkins, 1910)
- Glyptothorax siamensis (Hora, 1923)
- Glyptothorax silviae (Coad, 1981)[24]
- Glyptothorax sinensis (Regan, 1908)[25]
- Glyptothorax steindachneri (Pietschmann, 1913)
- Glyptothorax stocki (Mirza & Nijssen, 1978)[26]
- Glyptothorax stolickae (Steindachner, 1867)
- Glyptothorax strabonis (Ng & Freyhof, 2008)[16]
- Glyptothorax striatus (McClelland, 1842)
- Glyptothorax sufii (Asghar Bashir & Mirza, 1975)
- Glyptothorax telchitta (Hamilton, 1822)
- Glyptothorax tiong (Popta, 1904)
- Glyptothorax trewavasae (Hora, 1938)
- Glyptothorax trilineatus (Blyth, 1860)
- Glyptothorax ventrolineatus (Vishwanath & Linthoingambi, 2005)
- Glyptothorax zanaensis (Wu, He & Chu, 1981)
- Glyptothorax zhujiangensis (Lin, 2003)[27]
Referencias
- ↑ a b c Thomson, Alfred W.; Page, Lawrence M. (2006). «Genera of the Asian Catfish Families Sisoridae and Erethistidae (Teleostei: Siluriformes)» (PDF). Zootaxa 1345: pp. 1–96. http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2006f/zt01345p096.pdf.
- ↑ Ng, Heok Hee (2005). «Glyptothorax botius (Hamilton, 1822), a valid species of catfish (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from northeast India, with notes on the identity of G. telchitta (Hamilton, 1822)» (PDF). Zootaxa 930: pp. 1–19. http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2005f/zt00930.pdf.
- ↑ a b Ng, Heok Hee; Rachmatika, Ike (2005). «Glyptothorax exodon, a New Species of Rheophilic Catfish from Borneo (Teleostei: Sisoridae)» (PDF). The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology (2): pp. 251–255. http://rmbr.nus.edu.sg/rbz/biblio/53/53rbz251-255.pdf.
- ↑ BioLib (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ AQUATAB.NET (en checo). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ FishBase (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ Catalogue of Life (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ Discover Life (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ Dictionary of Common (Vernacular) Names (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ UNEP-WCMC Species Database (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ↑ Ng, H. H. 2005: Glyptothorax botius (Hamilton, 1822), a valid species of catfish (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from northeast India, with notes on the identity of G. telchitta (Hamilton, 1822). Zootaxa Núm. 930: 1-19.
- ↑ a b c Vishwanath, W. & Linthoingambi, I. (2007): Fishes of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from Manipur, India, with description of three new species. Zoos' Print Journal, 22 (3): 2617-2626.
- ↑ Ng, H.H. & Rainboth, W.J. 2008. Glyptothorax coracinus, a new species of hillstream catfish from Cambodia (Teleostei: Sisoridae). Zootaxa, 1839: 60–68.
- ↑ Manimekalan, A. y H. S. Das 1998: Glyptothorax davissinghi (Pisces: Sisoridae) a new cat fish from Nilambur in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, South India. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society v. 95 (pt 1): 87-91.
- ↑ Ng, H. H. & I. Rachmatika. 2005. Glyptothorax exodon, a new species of rheophilic catfish from Borneo (Teleostei: Sisoridae). Raffles Bull. Zool. v. 53 (núm. 2): 251-255.
- ↑ a b Ng, H.H. & Freyhof, J. 2008. Two new species of Glyptothorax (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from central Vietnam. Zootaxa, 1873: 11-25.
- ↑ Diogo, R., M. Chardon, y P. Vandewalle 2002: Osteology and myology of the cephalic region and pectoral girdle of Glyptothorax fukiensis (Rendahl, 1925), comparison with other sisorids, and comments on the synapomorphies of the Sisoridae (Teleostei: Siluriformes). Belgian Journal of Zoology v. 132 (núm. 2): 95-103.
- ↑ Herre, A. W. C. T. 1942: Glyptothorax housei, a new sisorid catfish from south India. Stanford Ichthyological Bulletin v. 2 (núm. 4): 117-119.
- ↑ Balon, E. K. y K. Hensel 1970: Notes on a small collection of fishes from Afganistan with a description of Glyptothorax jalalensis, sp. n. (Pisces, Sisoridae). Vestnik Ceskoslovenské Spolecnosti Zoologické v. 34 (núm. 3): 159-163.
- ↑ Biju, C. R., K. Raju Thomas, y C. R. Ajith Kumar 1998: Glyptothorax lonah (Sykes) -- an addition to the ichthyofauna of Kerala. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society v. 95 (pt 3): 519-520.
- ↑ Ferraris, C. J., Jr. & R. Britz. 2005. A diminutive new species of Glyptothorax (Siluriformes: Sisoridae) from the upper Irrawaddy River basin, Birmania, with comments on sisorid and erethistid phylogenetic relationships. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwaters v. 16 (núm. 4): 375-383.
- ↑ Ng, H.H. & Hadiaty, R.K. 2008. Glyptothorax plectilis, a new species of hillstream catfish from northern Sumatra (Teleostei: Sisoridae). Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 157: 137-147.
- ↑ Ng, H.H. 2008. Glyptothorax rugimentum, a new species of catfish from Birmania and Western Thailand (Teleostei: Sisoridae). The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 56 (1): 129-134.
- ↑ Coad, B. W. 1981: Glyptothorax silviae, a new species of sisorid catfish from southwestern Iran. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology v. 27 (núm. 4): 291-295.
- ↑ Xie, Z.-G., E. Zhang, y S.-P. He 2001: Study on species validation for Glyptothorax sinense (Regan) and Glyptothorax fukiensis (Rendahl) with the method of morphometrics. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University v. 20 (núm. 2): 169-172.
- ↑ Mirza, M. R. y H. Nijssen 1978: Glyptothorax stocki, a new sisorid catfish from Pakistan & Azad Kashmir (Siluriformes, Sisoridae). Bulletin Zoölogisch Museum, Universiteit van Amsterdam v. 6 (núm. 11): 79-85.
- ↑ Lin, Y.-H. 2003. A new species of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth from Guangdong, China (Siluriformes, Sisoridae). Acta Zootaxon. Sin. v. 28 (núm. 1): 159-162.
Bibliografía
- Burgess, W.E. 1989. An atlas of freshwater and marine catfishes. A preliminary survey of the Siluriformes. T.F.H. Publications, Inc., Neptune City, Nueva Jersey, Estados Unidos. 784 p.
- Eschmeyer, William N.: Genera of Recent Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. San Francisco, California, Estados Unidos. iii + 697. ISBN 0-940228-23-8. Año 1990.
- Eschmeyer, William N., ed. 1998. Catalog of Fishes. Special Publication of the Center for Biodiversity Research and Information, núm. 1, vol. 1-3. California Academy of Sciences. San Francisco, California, Estados Unidos. 2905. ISBN 0-940228-47-5.
- Ferraris, C. J., Jr. y R. Britz 2005: A diminutive new species of Glyptothorax (Siluriformes: Sisoridae) from the upper Irrawaddy River basin, Birmania, with comments on sisorid and erethistid phylogenetic relationships. Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters v. 16 (núm. 4): 375-383.
- Ferraris, Carl J.: Checklist of catfishes, recent and fossil (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes), and catalogue of siluriform primary types. Zootaxa, 1418. 8 de marzo del 2007. ISBN 978-1-86977-058-7. PDF (en inglés)
- Ganguly, D. N., N. C. Datta, y S. Sen 1972: Two new catfishes of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth (family: Sisoridae) from Subarnarekha River, Bihar, India. Copeia 1972 (núm. 2): 340-344.
- Helfman, G., B. Collette y D. Facey: The diversity of fishes. Blackwell Science, Malden, Massachusetts, Estados Unidos, 1997.
- Lin, Y.-H. 2003: A new species of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth from Guangdong, China (Siluriformes, Sisoridae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica v. 28 (núm. 1): 159-162.
- Mirza, M. R. y K. M. Kashmiri 1971: A note on the fishes of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth (Osteichthyes, Sisoridae) from West Pakistan with the description of a new subspecies. Biologia (Lahore) v. 17 (núm. 2): 87-93.
- Mo, T.-P. y X.-L. Chu 1986: A revision of the sisorid catfish genus Glyptothorax from China. Zoological Research v. 7 (núm. 4): 339-350.
- Moyle, P. y J. Cech.: Fishes: An Introduction to Ichthyology, 4a. edición, Upper Saddle River, Nueva Jersey, Estados Unidos: Prentice-Hall. Año 2000.
- Nelson, J.S. 2006: Fishes of the world. Cuarta edición. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, Nueva Jersey, Estados Unidos. 601 p.
- Silas, E. G. 1952: Notes on fishes of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth from Peninsular India, with description of a new species. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society v. 50 (pt 2) [1951]: 367-370.
- Tilak, R. y A. Husain 1976: Description of a new species of the genus Glyptothorax Blyth from River Yamuna, India (Pisces, Siluriformes: Sisoridae). Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) [Anales of Zoology] v. 33 (núm. 14): 229-234.
- Wheeler, A.: The World Encyclopedia of Fishes, 2a. edición, Londres: Macdonald. Año 1985.
Enlaces externos
- NCBI (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- ITIS (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- World Register of Marine Species (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- Encyclopedia of Life (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
- uBio (en inglés). Consultado en noviembre de 2010.
 Wikiespecies tiene un artículo sobre Glyptothorax. Wikispecies
Wikiespecies tiene un artículo sobre Glyptothorax. Wikispecies
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.
