- Integral de Gauss
-
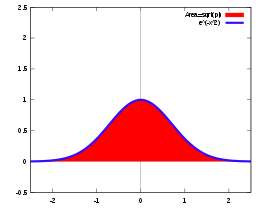
En matemáticas la integral de Gauss, integral gaussiana o integral de probabilidad, es la integral impropia de la función gaussiana
 sobre toda la recta de los reales. Debe su nombre al matemático y físico alemán Carl Friedrich Gauss, y su valor es:
sobre toda la recta de los reales. Debe su nombre al matemático y físico alemán Carl Friedrich Gauss, y su valor es:Esta integral tiene amplias aplicaciones, incluyendo normalización, en teoría de la probabilidad y transformada continua de Fourier. También aparece en la definición de la función error. A pesar de que no existe ninguna función elemental para la función error, como se puede demostrar mediante el algoritmo de Risch, la integral Gaussiana puede ser resuelta analíticamente con las herramientas del cálculo. O sea, no existe una integral indefinida elemental para
 , pero si es posible evaluar la integral definida
, pero si es posible evaluar la integral definida .
.Contenido
Cálculo de la integral
La forma más común de calcular la integral de Gauss en el plano R2 es mediante la integración doble en el sistema cartesiano de coordenadas, para después hacer un cambio de coordenadas a coordenadas polares y calcular el valor. Se procede de la siguiente manera:
- Mediante el teorema de Fubini, la integral puede ser escrita como:
- Pero también puede ser calculada mediante el cambio de coordenadas a coordenadas polares:
donde el factor r es consecuencia de calcular el determinante del cambio de las coordenadas cartesianas a polares, y s aparece al hacer un cambio de variable tal que s = - r2, ds = -2rdr. Así pues, obtenemos:
por lo tanto
Relación con la función gamma
Puesto que la integral gaussiana es una función par
lo cual, después de hacer un cambio de variable, se convierte en la Integral:
donde Γ es la función gamma. Esto muestra por qué el factorial de la mitad de un entero es un número racional múltiplo de
 . Más generalmente
. Más generalmenteGeneralizaciones
La integral de cualquier función Gaussiana es reducible en termino de la integral Gaussiana
la constante a puede ser factorizada fuera de la integral. Reemplazando x con y - b nos da:
sustituyendo y con cz nos da:
Referencias
- Weisstein, Eric W. «Gaussian Integral» (en inglés). MathWorld. Wolfram Research.
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.

 .
.  .
.








